Peripheral Artery Disease
Some wounds need more careful care, like those with poor blood supply or circulation
Your ability to heal from wound can be affected significantly if you do not have sufficient blood supply or circulation. This can put you at an increased risk of infection or ultimately the loss of a limb. If you are experience poor circulation due to peripheral arterial disease (PAD) you may need special care for your wound.
People with diabetes are often at a higher risk of developing PAD. Without proper care, an inquiry to the foot could lead to foot ulcers.
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) occurs when blood flow through the arteries is reduced because of narrowing and plaque buildup. It often happens in the legs and feet, but can also happen elsewhere in the body. If this buildup happens in the large artery in the neck (carotid artery), it can lead to stroke.
Is your limb at risk?
Over time when your leg arteries are damaged you may develop a severe form of peripheral arterial disease called critical limb ischemia (CLI). If blood flow to the toe, foot, or leg is completely blocked, the tissue starts to die (gangrene). If this happens, you need medical care right away to restore blood flow and possibly save the leg. But even with the best medical care, it might not be possible to save a severely affected limb.
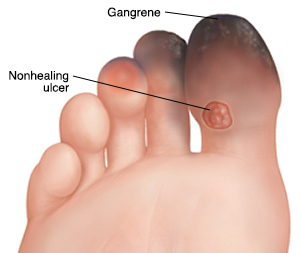
When do you need emergency care?
If left unchecked peripheral arterial disease can worsen and cause an urgent problem. For example, if you have a wound, it may not heal. This can lead to gangrene. Go to the emergency room right away if you have any of these symptoms:
- A wound that is foul smelling, draining pus, or discolored
- Severe foot or leg pain that occurs suddenly without injury, especially if the foot or leg is cold or numb
- Call your healthcare provider if:
- You have a cut or pressure injury that does not heal
- You have foot or leg pain that happens when walking but goes away with rest. This may be a sign of blocked arteries.
How is critical limb ischemia (CLI) diagnosed?
Certain tests may be done to find out if you have CLI. First your provider will carefully examine you, checking for pulses at several places. Other common tests include:
Ankle-brachial index (ABI). The blood pressure in your ankle is compared with the blood pressure in your arm.
Duplex ultrasound. Harmless sound waves are used to create images of blood flow in your legs.
Arteriography. X-ray dye (contrast medium) is injected into the artery using a thin, flexible tube (catheter). This allows blood vessels to be seen easily on X-rays.
How is it treated?
Possible treatments for CLI include:
- Dissolving or removing a blood clot. To dissolve a clot, a tube (catheter) is put into an artery in your groin. Clot-busting medicine is put into the tube to dissolve the clot. Or surgery may be done to remove the clot. A cut (incision) is
made in the artery at the blocked area. The clot is then removed.
- Angioplasty. A tiny, uninflated balloon is sent to the narrowed area by a catheter. It's then inflated to widen the artery. The balloon is deflated and removed.
- Stenting. After angioplasty, a tiny wire mesh tube (stent) may be put in the artery to help hold it open. The stent is also put in using a catheter.
- Endarterectomy. An incision is made in the artery at the blocked area. The material that blocks the artery is then removed from artery walls.
- Peripheral bypass surgery. A natural or artificial graft is used to bypass the blocked area.
- Amputation. If left untreated, the affected area may have to be removed (amputated).
How can critical limb ischemia emergencies be prevented?
Know the signs and symptoms of a leg artery emergency. If you have diabetes or poor blood circulation, check your feet daily for wounds, sores, blisters, and color changes. If you smoke, get help to stop.