Bronchitis, No Antibiotics (Adult)
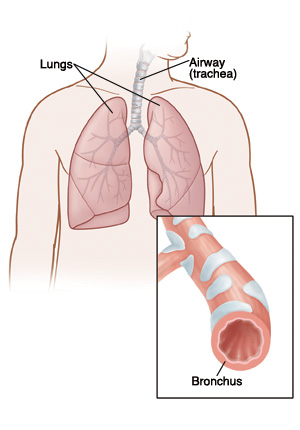
Bronchitis is inflammation and swelling of the air passages (bronchial tubes) in your lungs. This is often caused by an infection. Your bronchitis was caused by a virus. Symptoms include a dry, hacking cough that is worse at night. The cough may bring up yellow-green mucus. You may also feel short of breath or wheeze. Other symptoms may include tiredness, chest discomfort, fever, and chills.
This illness can be spread to other people in the first few days. It is spread through the air by coughing and sneezing. It is also spread by direct contact. This means touching the sick person and then touching your own eyes, nose, or mouth.
Bronchitis that is caused by a virus is often not treated with antibiotic medicine. Instead, medicines may be given to help relieve symptoms. Symptoms can last up to 2 weeks. The cough may last much longer.
Home care
Follow these guidelines when caring for yourself at home:
-
If your symptoms are severe, rest at home for the first 2 to 3 days. When you go back to your daily tasks, don't let yourself get too tired.
-
Do not smoke. Stay away from secondhand smoke.
-
You may use over-the-counter medicine to control fever or pain. Or use another pain medicine as prescribed. If you have chronic liver or kidney disease or have ever had a stomach ulcer or bleeding in your stomach or intestines, talk with your healthcare provider before using these medicines. Also talk to your provider if you are taking medicine to prevent blood clots. Aspirin should never be taken by anyone under age 18 who has a virus or fever. It may cause severe liver or brain damage.
-
Your body needs a lot of fluids now. Drink 6 to 8 glasses of fluids per day. This includes water, soft drinks, sports drinks, juices, tea, or soup. Extra fluids will help loosen mucus in your nose and lungs.
-
Your appetite may be low. A light diet is fine.
-
Over-the-counter cough, cold, and sore-throat medicines will not shorten the length of the illness. But they may help to reduce your symptoms. Don't use decongestants if you have high blood pressure.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your healthcare provider, or as advised. If you had an X-ray or ECG (electrocardiogram), a specialist will review it. You will be told of any results that may affect your care.
Ask your healthcare provider about the pneumococcal vaccines and a yearly flu shot. There are 2 kinds of pneumococcal vaccines. You may need both. You’re at higher risk of lung infection if any of these apply to you:
When to get medical care
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these:
-
Fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher
-
Coughing up more mucus
-
Facial pain or ear pain
-
Mild weakness, drowsiness, headache, or a stiff neck
Call 911
Call 911 if any of these occur:
-
Coughing up blood
-
Weakness, drowsiness, headache, or stiff neck that get worse
-
Trouble breathing, wheezing, or pain with breathing
-
Lips or skin looks blue, purple, or gray in color
-
Feeling of doom